What is monkeypox?
Monkeypox is a rare viral infection that comes from certain animals, most likely certain species of rodents in deep forest areas of some countries in the Western and Central Africa Region. The virus may occasional spill over from the infected animals to humans. There is no rest of monkeypox infections from animals in South Africa. When a person is infected by an animal, person-to-person would happen when they come into close contact.
Can people die from monkeypox?
In most case, the symptoms of monkeypox go away on their own within a few weeks, but in some individuals, they could lead to medical complications and even result in death. New born children and people with underlying immune deficiencies may be at risk of more serious symptoms and death from monkeypox.
Complications from severe cases of monkeypox include skin infections, pneumonia, confusion and eye infections which can lead to loss of vision. Around 3 to 6% of reported cases have led to death in endemic countries in recent times, often in children or persons who may have other health conditions. It is important to note that this may be an overestimate because surveillance in endemic countries is limited.
How does monkeypox spread from person to person?
People with monkeypox are infectious while they still show symptoms (between two and four weeks). You can catch monkeypox through physical contact with a person who is infected. The rash, bodily fluids and scabs are contagious. Ulcer, or sores in the mouth can also be infectious, meaning the virus can spread through saliva. You can be infected if you come to very close physical contact with someone, through kissing, touching or having sexual intercourse with the infected person.
The virus can also spread from someone who is pregnant to the foetus from the placenta, or from an infected parent to child during or after birth through skin-to-skin contact.
How is it treated?
Most human cases of monkeypox do not require any specific treatment and the disease vanishes on its own. Treatment is symptomatic and a doctor may prescribe medication to ease your pain and any other discomfort. It is important to stay hydrated and avoid scratching or bursting the blisters to prevent infection with bacteria.
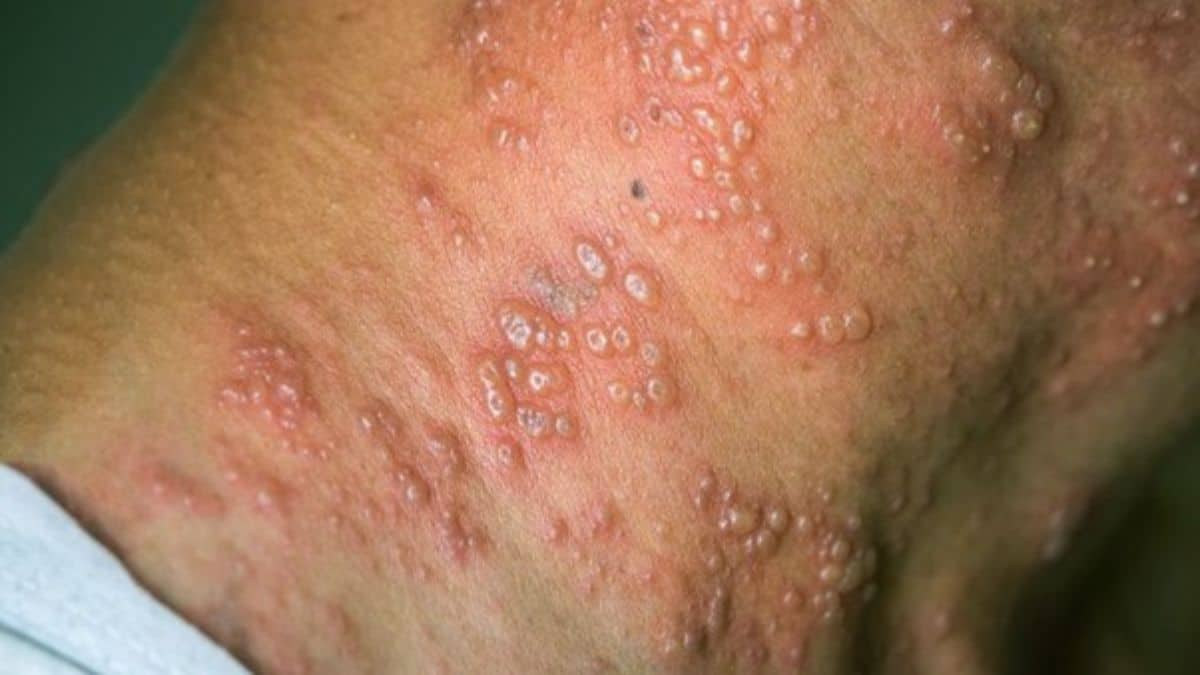
How will you know if you have monkeypox?
A rash can look like pimples that appears on the face, inside your mouth, and on other parts of the body, like on your hands, feet chest, genitals or anus. Some people get the rash first and show symptoms later and vice versa.
Source: National Institute for Communicable Diseases, World Health Organisation, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, image from Twitter